Infinite Charged Sheet - Therefore only the ends of a cylindrical. This is independent of the distance of p from the infinite charged sheet. Web e = σ 2ϵ0. Web an infinite sheet of charge consider an infinite sheet of charge with uniform charge density per unit area s. (1.6.12) (1.6.12) e = σ 2 ϵ 0. Web for an infinite sheet of charge, the electric field will be perpendicular to the surface.
Web an infinite sheet of charge consider an infinite sheet of charge with uniform charge density per unit area s. Therefore only the ends of a cylindrical. (1.6.12) (1.6.12) e = σ 2 ϵ 0. This is independent of the distance of p from the infinite charged sheet. Web for an infinite sheet of charge, the electric field will be perpendicular to the surface. Web e = σ 2ϵ0.
Web e = σ 2ϵ0. Web an infinite sheet of charge consider an infinite sheet of charge with uniform charge density per unit area s. This is independent of the distance of p from the infinite charged sheet. Web for an infinite sheet of charge, the electric field will be perpendicular to the surface. (1.6.12) (1.6.12) e = σ 2 ϵ 0. Therefore only the ends of a cylindrical.
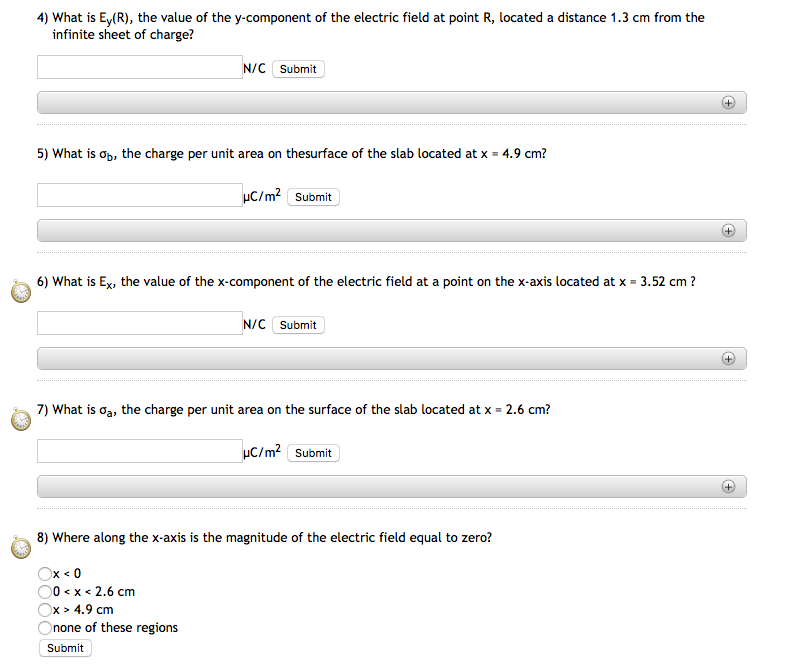
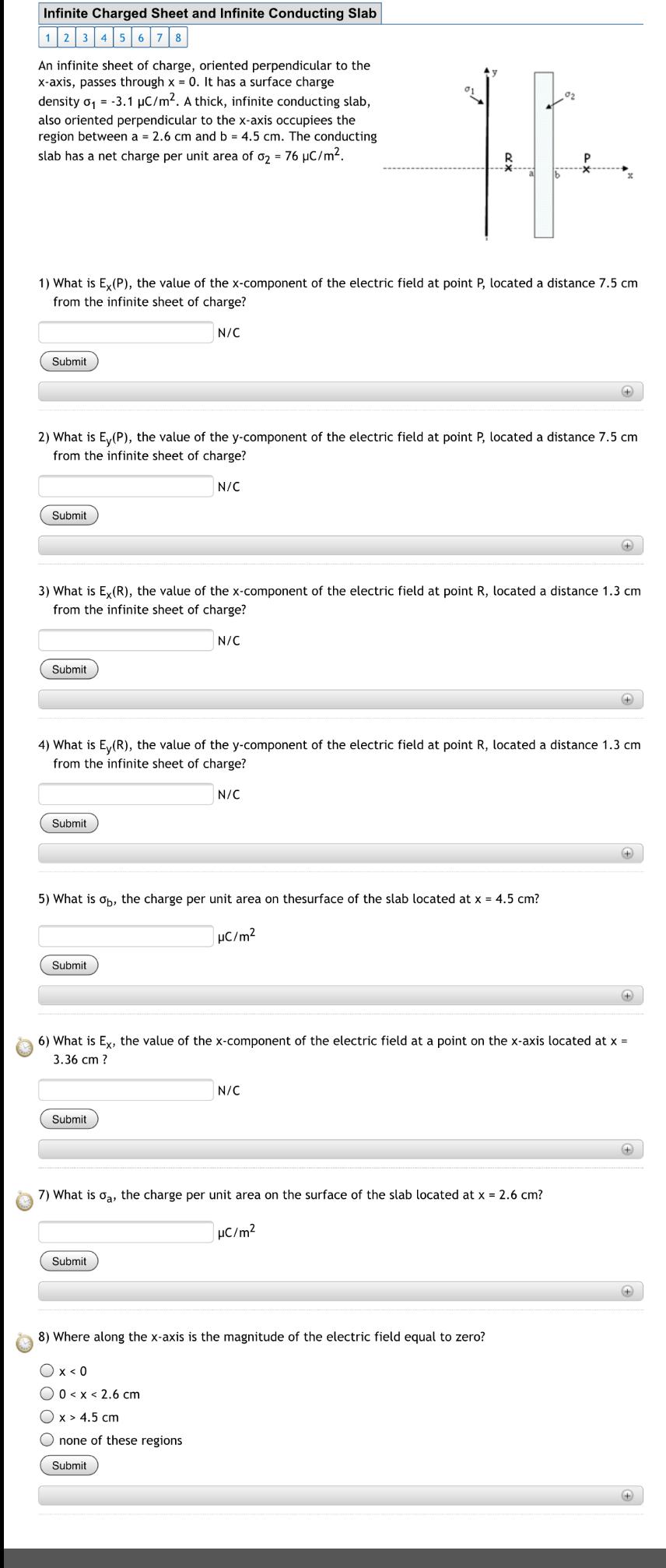
Solved Infinite Charged Sheet and Infinite Conducting Slab 1
Web an infinite sheet of charge consider an infinite sheet of charge with uniform charge density per unit area s. (1.6.12) (1.6.12) e = σ 2 ϵ 0. Web e = σ 2ϵ0. Therefore only the ends of a cylindrical. Web for an infinite sheet of charge, the electric field will be perpendicular to the surface.
Solved Infinite charged sheet with a circular hole. An infinit
Web an infinite sheet of charge consider an infinite sheet of charge with uniform charge density per unit area s. Therefore only the ends of a cylindrical. Web for an infinite sheet of charge, the electric field will be perpendicular to the surface. Web e = σ 2ϵ0. This is independent of the distance of p from the infinite charged.
Electric Field Of An Infinite Line
This is independent of the distance of p from the infinite charged sheet. Web for an infinite sheet of charge, the electric field will be perpendicular to the surface. (1.6.12) (1.6.12) e = σ 2 ϵ 0. Web e = σ 2ϵ0. Web an infinite sheet of charge consider an infinite sheet of charge with uniform charge density per unit.
electric field intensity due to infinite uniformly charged conducting
(1.6.12) (1.6.12) e = σ 2 ϵ 0. Web e = σ 2ϵ0. Web for an infinite sheet of charge, the electric field will be perpendicular to the surface. Web an infinite sheet of charge consider an infinite sheet of charge with uniform charge density per unit area s. Therefore only the ends of a cylindrical.
Solved Infinite Charged Sheet and Infinite Conducting Slab
Web e = σ 2ϵ0. This is independent of the distance of p from the infinite charged sheet. Web for an infinite sheet of charge, the electric field will be perpendicular to the surface. Web an infinite sheet of charge consider an infinite sheet of charge with uniform charge density per unit area s. Therefore only the ends of a.
A particle A of charge q placed near a uniformly charged infinite plane
(1.6.12) (1.6.12) e = σ 2 ϵ 0. Web e = σ 2ϵ0. Web an infinite sheet of charge consider an infinite sheet of charge with uniform charge density per unit area s. Web for an infinite sheet of charge, the electric field will be perpendicular to the surface. This is independent of the distance of p from the infinite.
Electric Field due to Uniformly Charged Infinite Plane Sheet and Thin
Therefore only the ends of a cylindrical. Web for an infinite sheet of charge, the electric field will be perpendicular to the surface. (1.6.12) (1.6.12) e = σ 2 ϵ 0. Web e = σ 2ϵ0. Web an infinite sheet of charge consider an infinite sheet of charge with uniform charge density per unit area s.
Application of Gauss' Theorem Electric Field near Charged Infinite
Web e = σ 2ϵ0. Web for an infinite sheet of charge, the electric field will be perpendicular to the surface. Therefore only the ends of a cylindrical. Web an infinite sheet of charge consider an infinite sheet of charge with uniform charge density per unit area s. (1.6.12) (1.6.12) e = σ 2 ϵ 0.
Electric Field Intensity of an Infinite Sheet of Charge YouTube
(1.6.12) (1.6.12) e = σ 2 ϵ 0. Web an infinite sheet of charge consider an infinite sheet of charge with uniform charge density per unit area s. Web for an infinite sheet of charge, the electric field will be perpendicular to the surface. Therefore only the ends of a cylindrical. Web e = σ 2ϵ0.
Solved Infinite Charged Sheet and Infinite Conducting Slab
Web for an infinite sheet of charge, the electric field will be perpendicular to the surface. Web e = σ 2ϵ0. Web an infinite sheet of charge consider an infinite sheet of charge with uniform charge density per unit area s. This is independent of the distance of p from the infinite charged sheet. (1.6.12) (1.6.12) e = σ 2.
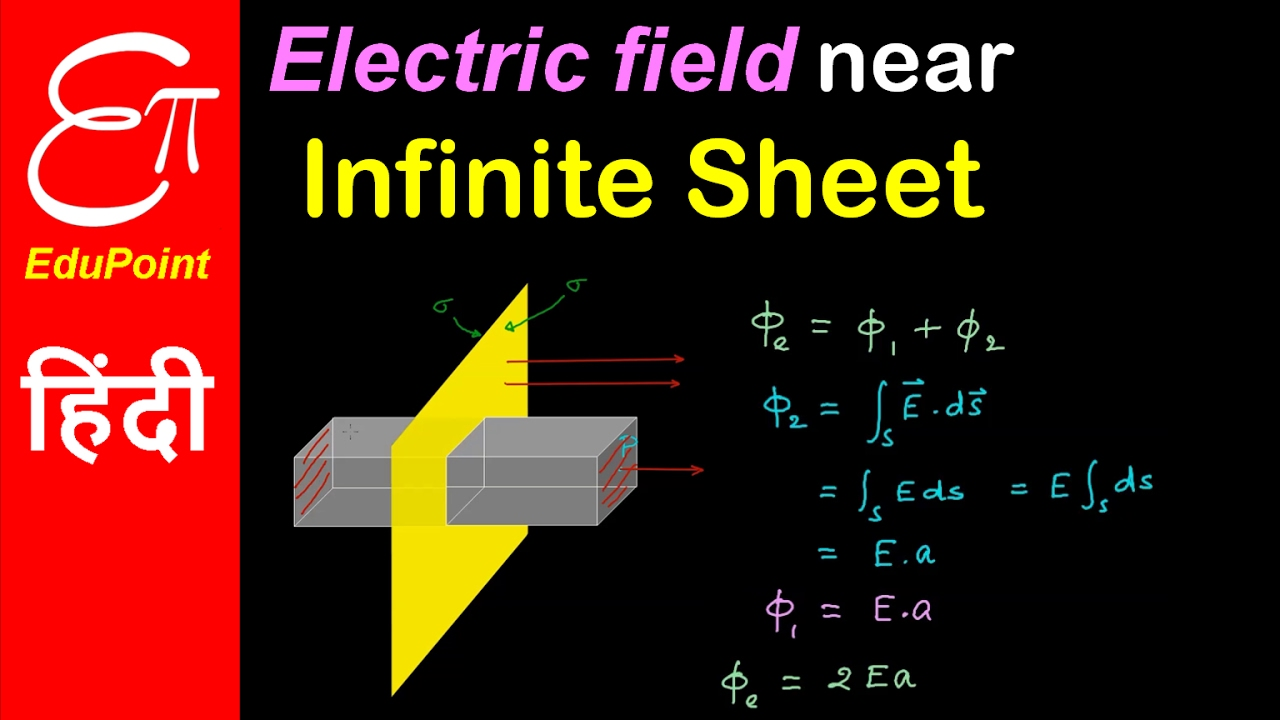
Web For An Infinite Sheet Of Charge, The Electric Field Will Be Perpendicular To The Surface.
Web e = σ 2ϵ0. Web an infinite sheet of charge consider an infinite sheet of charge with uniform charge density per unit area s. (1.6.12) (1.6.12) e = σ 2 ϵ 0. Therefore only the ends of a cylindrical.